- Year Present
- Theme Financial Inclusion
- Team Special Projects
Partnerships
- India Post Payment Bank (IPPB)
- Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation


India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) wants to increase the number of transactions facilitated by its banking agents (also referred to as GDS or 'End Users' (EUs)). During the initial research, banking agents' motivation emerged as a key barrier for the same. While banking agents' motivation was linked to multiple levers, better communication of incentives was identified as the significant lever. With this background, CSBC designed a pilot which focussed on simplifying communication around incentives and improving the dissemination within the banking agents of the Delhi and Bihar circles.
The India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) was set up under the Department of Post, Ministry of Communication, in response to the new model of payment banks proposed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in November 2014. It was designed to leverage the Department of Posts (DoP) field network to offer payment bank services to the rural population, using Door-step assisted banking and regular counter services through postmen or Gramin Dak Sevaks (GDS).
Banking agents deliver financial services to their customers. However, incentive-related communication is not centralised and instead happens via circle offices. This results in non-standardised communication with banking agents. This project aims to improve banking agents' motivation through behaviourally-informed interventions focused on improved communication and dissemination of incentive schemes. CSBC conducted learning sessions with circle heads of better-performing circles to learn the best practices to design the interventions.
To begin the pilot, the team conducted detailed sessions with circle staff to explain the intervention. In this session, we encouraged IPPB staff to form the required WhatsApp groups for communications. All the communication material developed by CSBC was communicated to the groups via IPPB staff.
CSBC designed the following intervention package for the pilot:
We ran the pilot for three weeks in March 2022 in two circles of IPPB. The branch managers had to do the following four interventions daily:
CSBC supported the branch managers by telling them what to share on the WhatsApp group. The team also shared talking points with the branch manager to speak to the agents.
The pilot showed promising results, especially in the Bihar circle and rural branches. In Bihar, there was a ~392% increase in Child Enrolment Lite Client (CELC) transactions in pilot branches compared to 227% in control branches. We observed a significant jump (up to 542% in Lakhisarai, Bihar branch) in the number of transactions in three out of four pilot branches.
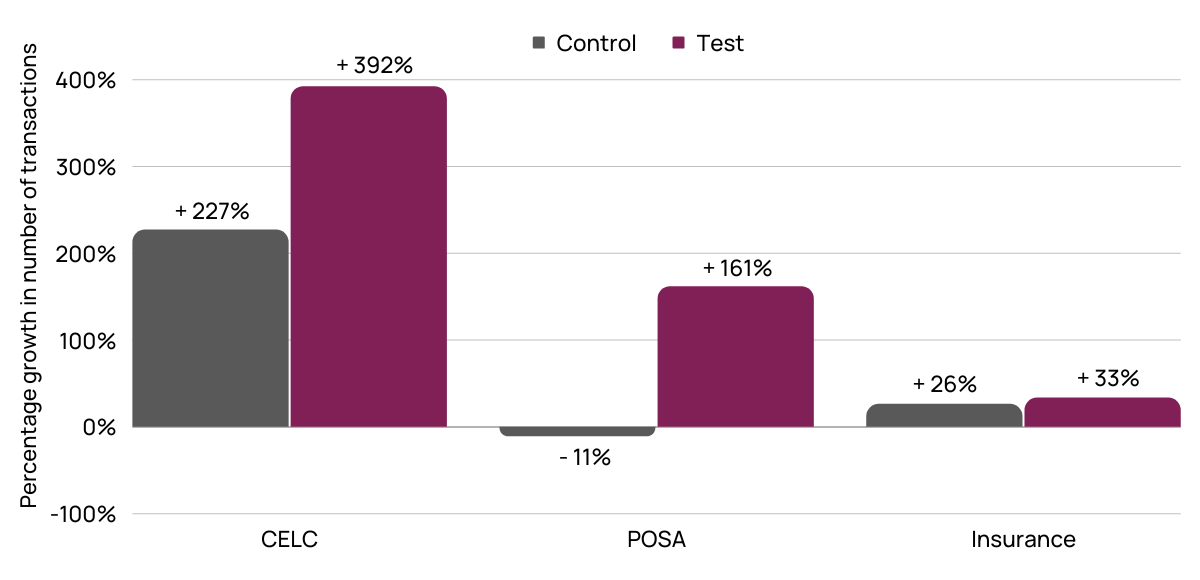
Percentage growth in the number of transactions during the pilot period for control and test branches, Bihar circle
The Delhi circle had a mixed performance, with semi-rural branches showing significant increases (an increase of 268% was reported for Post Office Savings Account (POSA) transactions). We believe that effective communication has improved engagement and awareness in banking agents based in rural and semi-rural areas compared to urban areas.
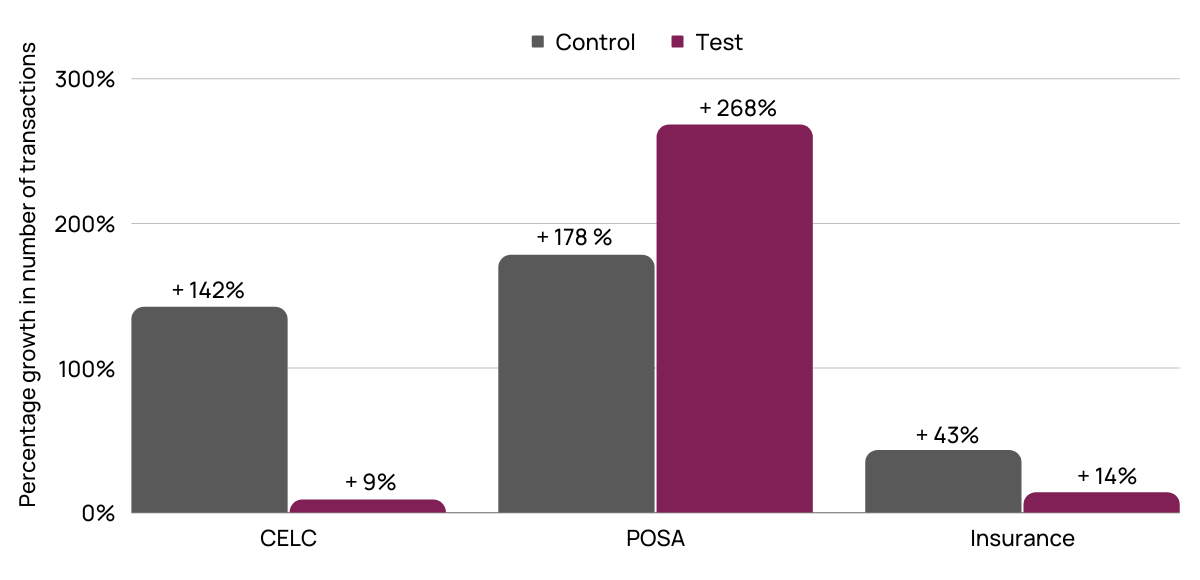
Percentage growth in the number of transactions during the pilot period for control and test branches, Delhi circle
We designed the pilot by studying best practices from high-performing circles (e.g., Telangana).
We defined a baseline for Bihar and Delhi; interventions were conducted over 3 weeks. We also
conducted qualitative research to identify other systemic issues faced by the staff and banking
agents.
For the pilot, the CSBC team designed flyers, short videos, and a web-based incentive
calculator. The pilot was conducted in two phases. Phase 1 is in the Bihar circle, and Phase 2
is in the Delhi circle. CSBC measured the impact of interventions by analysing changes in
incentives earned by banking agents. Based on the pilot, CSBC provided behaviourally-informed
recommendations for improving the overall motivation levels of agents by modifying incentive
communication.